Environment Import & Export
Version: 4.22+
Environment export and import lets you copy feature configurations from one environment to another and even copy features from one Unleash instance to another.
When exporting, you select a set of features and one environment to export the configuration from. The environment must be the same for all features.
Then, when you import, you must select one environment and one project to import into. All features are imported into that project in that environment. If Unleash is unable to import the configuration safely, it will tell you why the import failed and what you need to fix it (read more about import requirements.
Import & Export items
When you export features, the export will contain both feature-specific configuration and global configuration.
On the project-level these items are exported:
On the environment-level, these items are exported for the chosen environment:
- activation strategies including constraints and references to segments
- variants
- enabled/disabled
Additionally, these global configuration items are exported:
Importantly, while references to segments are exported, the segments themselves are not exported. Consult the import requirements section for more information.
Export
You can export features either from a project search or the global feature search. Use the search functionality to narrow the results to the list of features you want to export and use the export button to select environment. All features included in your search results will be included in the export.
Import
Import is a 3 stage process designed to be efficient and error-resistant.
Import stages
- upload - you can upload previously exported JSON file or copy-paste export data from the exported JSON file into the code editor
- validation - you will get feedback on any errors or warnings before you do the actual import. This ensures your feature flags configurations are correct. You will not be able to finish the import if you have errors. Warnings don't stop you from importing.
- import - the actual import that creates a new configuration in the target environment or creates a [change request]/reference/change-requests.md) when the environment has change requests enabled
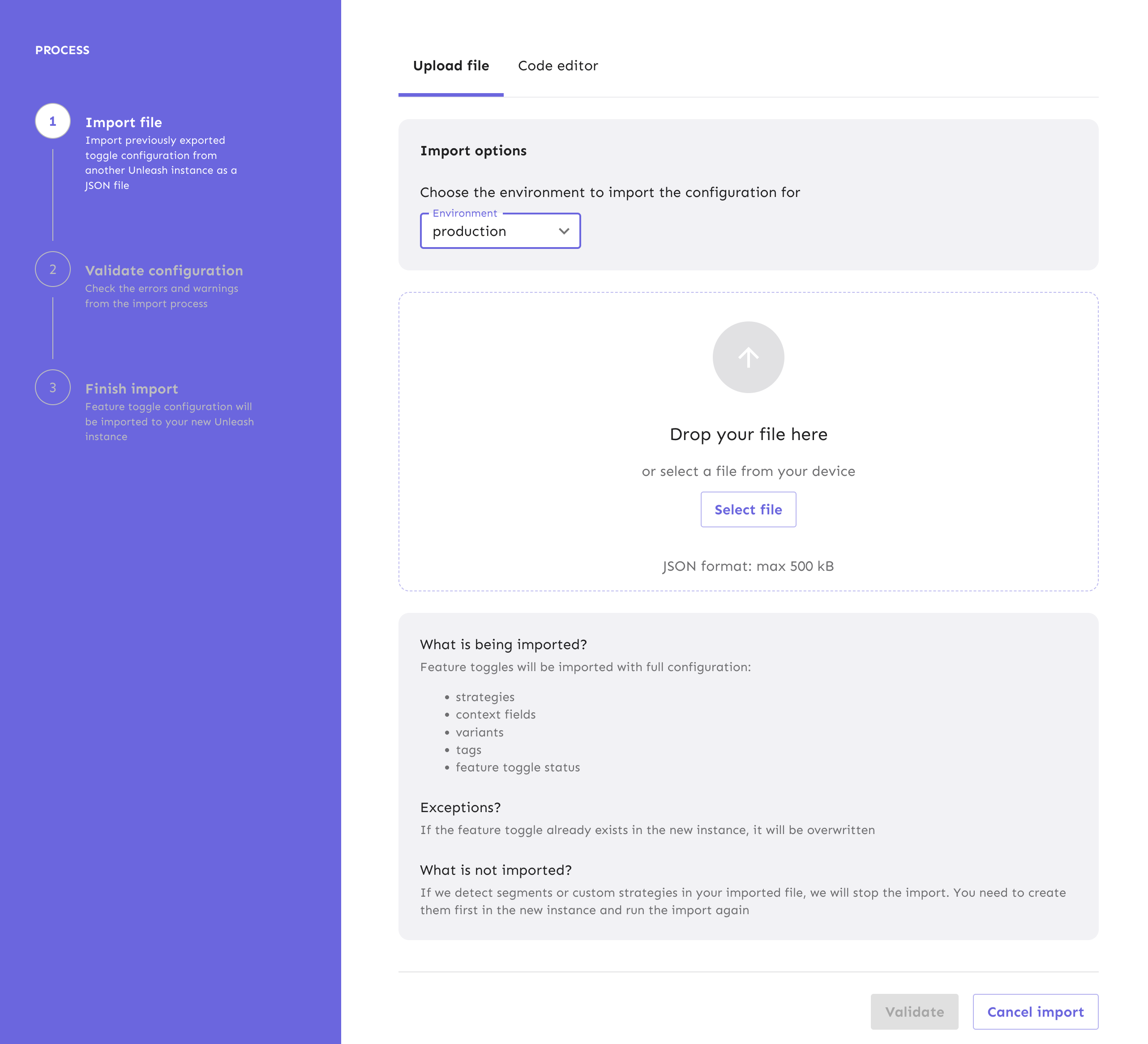
Import requirements
Unleash will reject an import if it discovers conflicts between the data to be imported and what already exists on the Unleash instance. The import tool will tell you about why an import is rejected in these cases.
The following sections describe requirements that must be met for Unleash not to stop the import job.
Context fields
When you import a custom context field with legal values defined:
If a custom context field with the same name already exists in the target instance, then the pre-existing context field must have at least those legal values defined. In other words, the imported context field legal values must be a subset of the already existing context field's legal values.
When you import custom context fields without legal values or custom context fields that don't already exist in the target instance, then there are no requirements.
Custom context fields that don't already exist in the target instance will be created upon import.
Segments
If your import has segments, then a segment with the same name must already exist in the Unleash instance you are trying to import into. Only the name must be the same: the constraints in the segment can be different.
Dependencies
If your import has a parent feature dependency, then the parent feature must already exist in the target Unleash instance or be part of the import data. The existing feature is identified by name.
Custom strategies
If your import contains custom strategies, then custom strategies with the same names must already exist in the target Unleash instance. The custom strategy definitions (including strategy parameters) that exist in the target instance do not otherwise need to match the custom strategy definitions in the instance the import came from.
Existing features
If any of the features you import already exist in the target Unleash instance, then they must exist within the project you're importing into. If any features you are attempting to import exist in a different project on the target instance, the import will be rejected.
Pending change requests
The project and environment you are importing into must not have any pending change requests.
Import warnings
The import validation system will warn you about potential problems it finds in the import data. These warnings do not prevent you from importing the data, but you should read them carefully to ensure that Unleash does as you intend.
The following sections list things that the import tool will warn you about.
Archived features
The import tool will not import any features that have already been archived on the target Unleash instance. Because features are identified by their name, that means that if a feature called feature-a has been created and archived on the target Unleash instance, then a feature with the same name (feature-a) will not be imported.
If you permanently delete the archived feature-a from the target instance, then the new feature-a (in the import data) will be imported.
Custom strategies
Unleash will verify that any custom strategies you are trying to import have already been defined on the target instance. However, it only does this verification by name. It does not validate that the definitions are otherwise the same or that they have the same configuration parameters.
Required permissions
To import features, you will always require the update feature flags permission. Additionally, depending on the actions your import job would trigger, you may also require any of the following permissions:
- Create feature flags: when the import would create new features
- Update tag types: when the import would create new tag types
- Create context fields: when the import would create new context fields
- Create activation strategies: when the import would add activation strategies to a feature and change requests are disabled
- Delete activation strategies: when import would remove existing activation strategies from a feature and change requests are disabled
- Update variants: when the import would update variants and change requests are disabled
- Update feature dependency: when the import would add feature dependencies and change requests are disabled
Import and change requests
If change requests are enabled for the target project and environment, the import will not be fully applied. Any new features will be created, but all feature configuration will be added to a new change request.
If change requests are enabled, any permissions for Create activation strategies, Delete activation strategies and Update variants are not required.
Environment import/export vs the instance import/export API
Environment import/export has some similarities to the instance import/export API, but they serve different purposes.
The instance import/export API was designed to export all feature flags (optionally with strategies and projects) from one Unleash instance to another. When it was developed, Unleash had much fewer features than it does now. As such, the API lacks support for some of the more recent features in Unleash.
On the other hand, the environment import/export feature was designed to export a selection of features based on search criteria. It can only export data from a single environment and only import it to a single environment. It also only supports importing into a single project (although it can export features from multiple projects).
Further, the environment import/export comes with a much more stringent validation and will attempt to stop any corrupted data imports.
Startup import
You can also import on startup by using an import file in JSON format and the import will be applied on top of existing data. Currently the startup import supports the same data supported in OSS import.
Unleash lets you do this both via configuration parameters and environment variables. The relevant parameters/variables are:
| config parameter | environment variable | default | value |
|---|---|---|---|
file | IMPORT_FILE | none | path to the configuration file |
project | IMPORT_PROJECT | default | which project to import into |
environment | IMPORT_ENVIRONMENT | development | which environment to import for |